Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems.
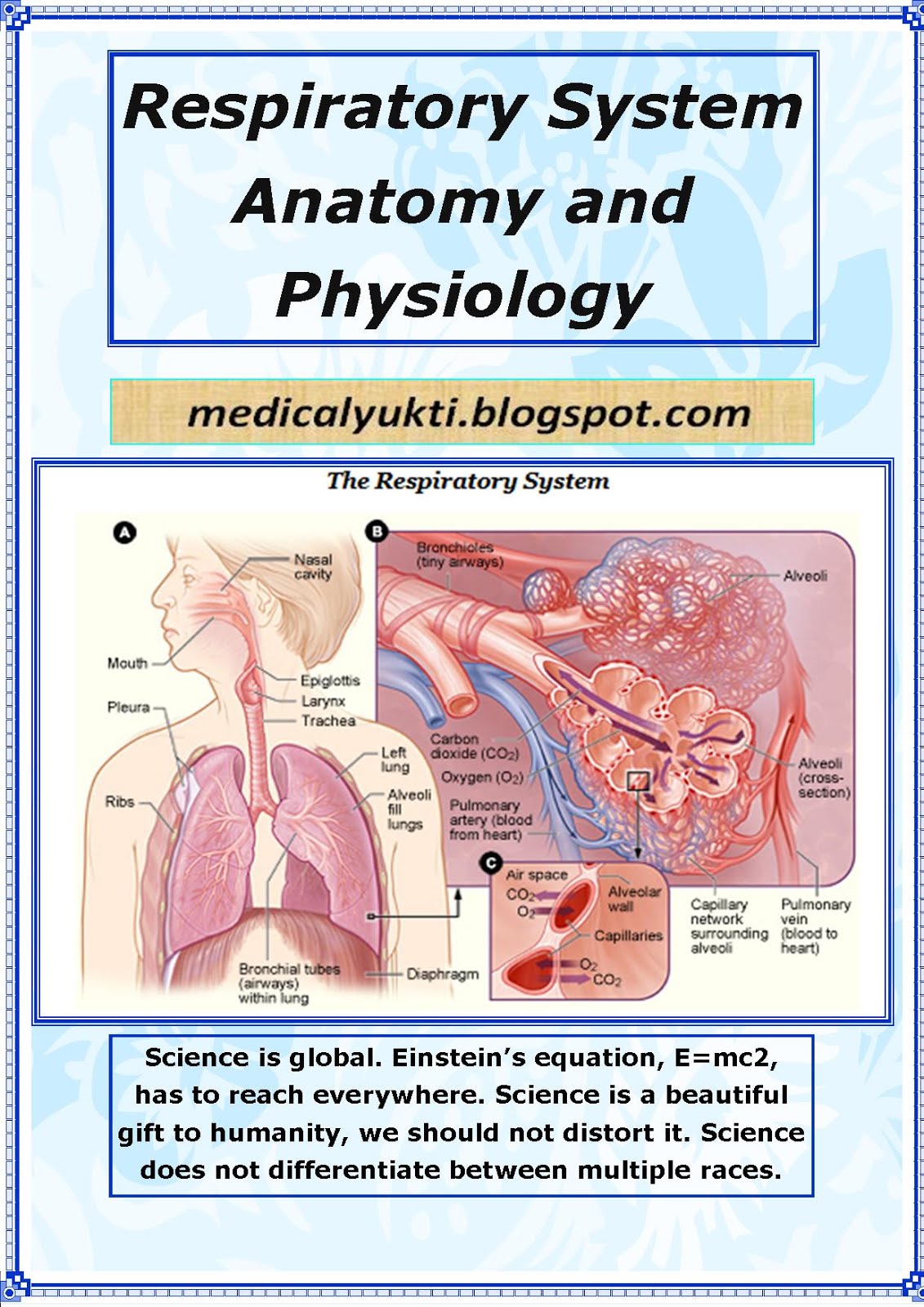
Biochemistry focuses on processes happening at a molecular level. It focuses on what’s happening inside our cells, studying components like proteins, lipids and organelles. It also looks at how cells communicate with each other, for example during growth or fighting illness. Biochemists need to understand how the structure of a molecule relates to its function, allowing them to predict how molecules will interact.
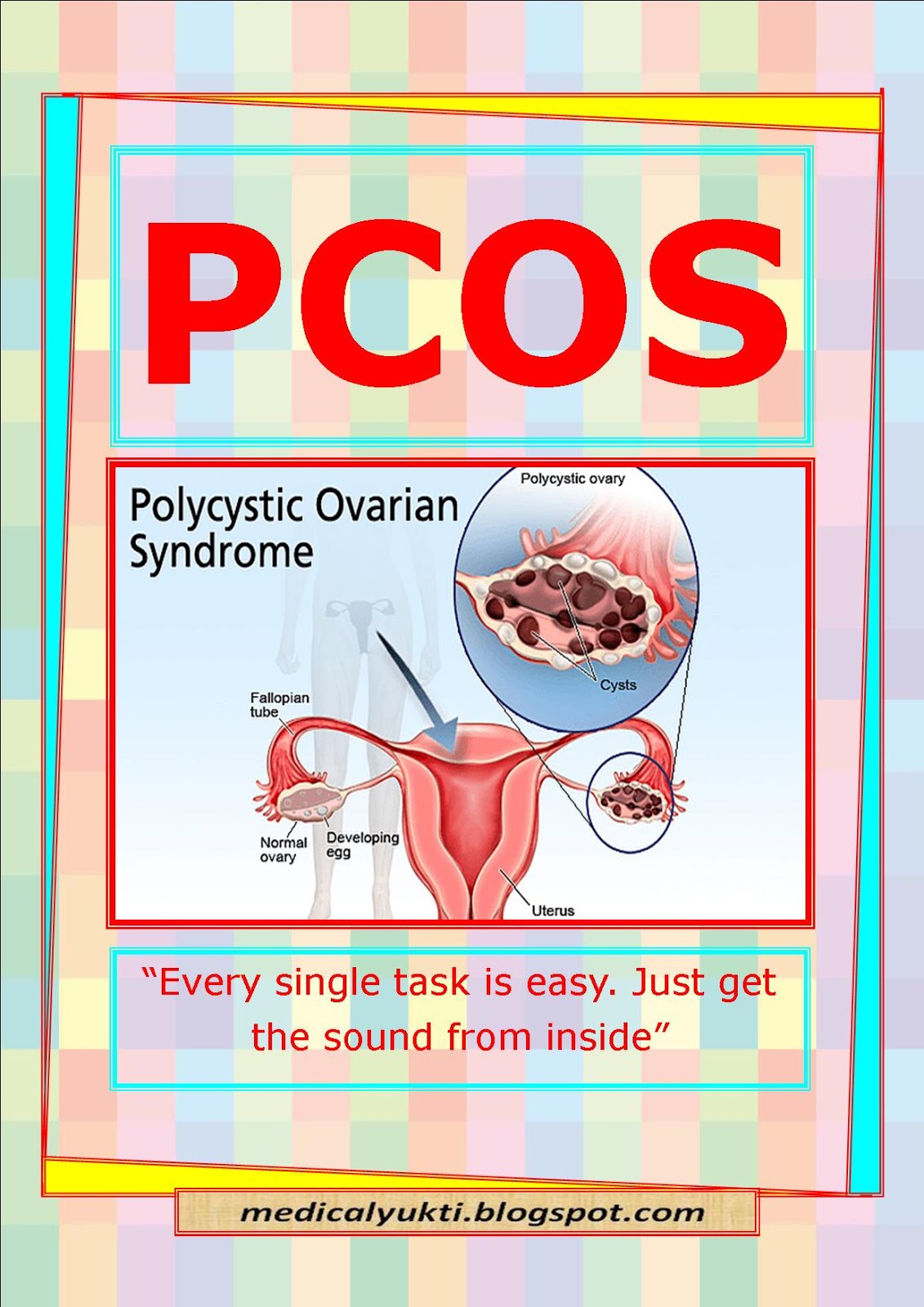
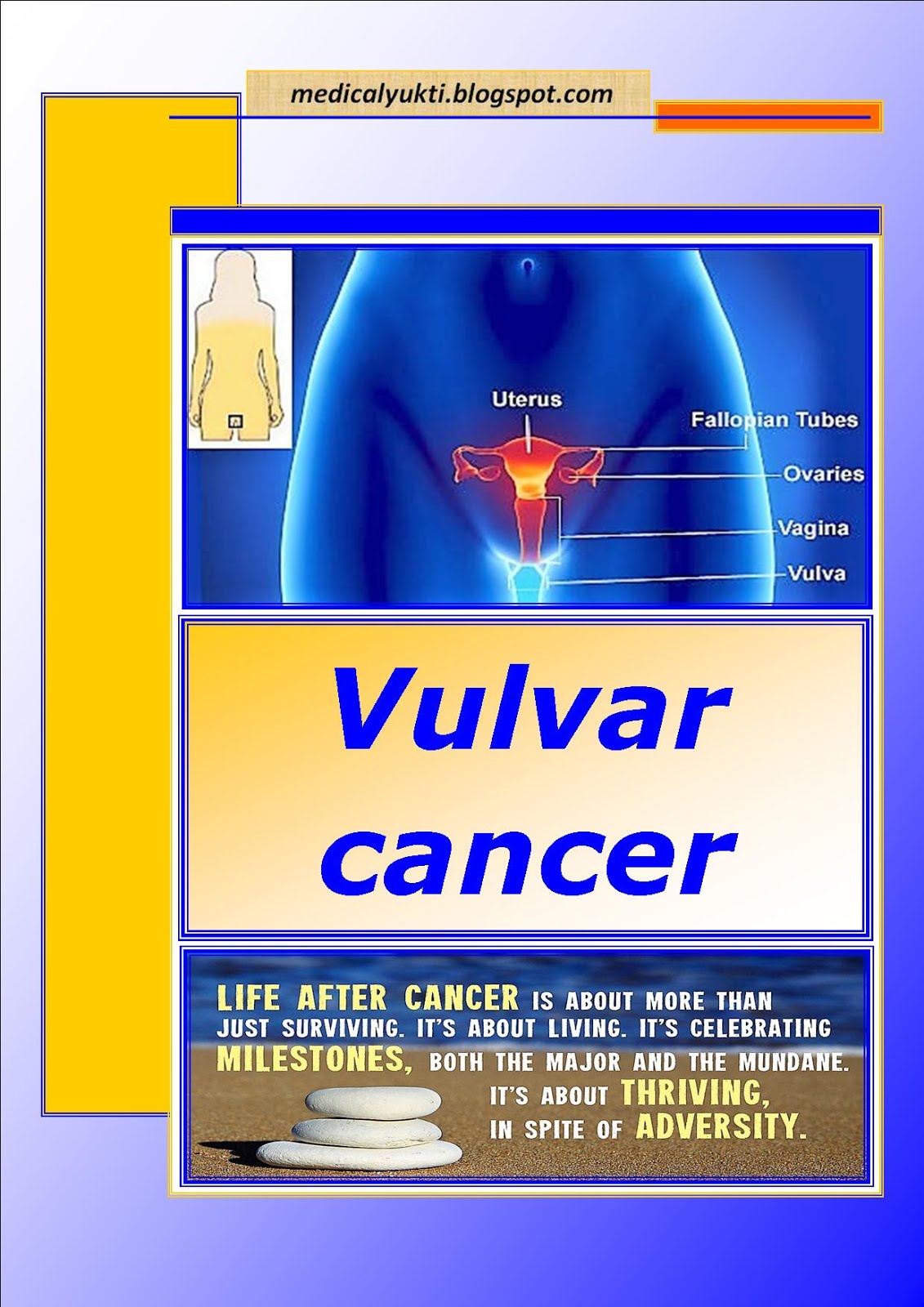
Biochemistry covers a range of scientific disciplines, including genetics, microbiology, forensics, plant science and medicine. Because of its breadth, biochemistry is very important and advances in this field of science over the past 100 years have been staggering. It’s a very exciting time to be part of this fascinating area of study.